Nimodipine
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nimotop |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a689010 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Intravenous, Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 13% (Oral) |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 8–9 hours |
| Excretion | Feces and Urine |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.060.096 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
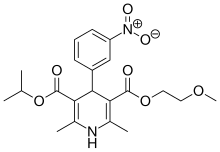
| Formula | C21H26N2O7 |
| Molar mass | 418.44 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Melting point | 7 °C (45 °F) |
|
|
|
|
Nimodipine (marketed by Bayer as Nimotop) is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker originally developed for the treatment of high blood pressure. It is not frequently used for this indication, but has shown good results in preventing a major complication of subarachnoid hemorrhage (a form of cerebral hemorrhage) termed vasospasm; this is now the main use of nimodipine.
The regular dosage is 60 mg tablets every four hours. If the patient is unable to take tablets orally, it was previously given via intravenous infusion at a rate of 1–2 mg/hour (lower dosage if the body weight is <70 kg or blood pressure is too low), but since the withdrawal of the IV preparation, administration by nasogastric tube is an alternative.
Because it has some selectivity for cerebral vasculature, nimodipine's main use is in the prevention of cerebral vasospasm and resultant ischemia, a complication of subarachnoid hemorrhage (a form of cerebral bleed), specifically from ruptured intracranial berry aneurysms irrespective of the patient's post-ictus neurological condition. Its administration begins within 4 days of a subarachnoid hemorrhage and is continued for three weeks. If blood pressure drops by over 5%, dosage is adjusted. There is still controversy regarding the use of intravenous nimodipine on a routine basis.
A 2003 trial (Belfort et al.) found nimodipine was inferior to magnesium sulfate in preventing seizures in women with severe preeclampsia.
Nimodipine is not regularly used to treat head injury. Several investigations have been performed evaluating its use for traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage; a systematic review of 4 trials did not suggest any significant benefit to the patients that receive nimodipine therapy. There was one report case of nimodipine being successfully used for treatment of ultradian bipolar cycling after brain injury and, later, amygdalohippocampectomy.
...
Wikipedia
