Neurogenic shock
| Neurogenic shock | |
|---|---|
 |
|
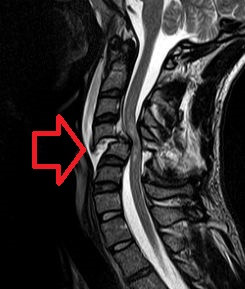
| Cervical spine MRI of a patient with SCI: C4 fracture and dislocation, spinal cord compression | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | R57.8 |
| ICD-9-CM | 785 |
| MeSH | D012769 |
Neurogenic shock is a distributive type of shock resulting in low blood pressure, occasionally with a slowed heart rate, that is attributed to the disruption of the autonomic pathways within the spinal cord. It can occur after damage to the central nervous system such as spinal cord injury. Low blood pressure occurs due to decreased systemic vascular resistance resulting in pooling of blood within the extremities lacking sympathetic tone. The slowed heart rate results from unopposed vagal activity and has been found to be exacerbated by hypoxia and endobronchial suction. Neurogenic shock can be a potentially devastating complication, leading to organ dysfunction and death if not promptly recognized and treated. It is not to be confused with spinal shock, which is not circulatory in nature.
Neurogenic shock can result from severe central nervous system damage (brain injury, cervical or high thoracic spinal cord). In more simple terms: the trauma causes a sudden loss of background sympathetic stimulation to the blood vessels. This causes them to relax (vasodilation) resulting in a sudden decrease in blood pressure (secondary to a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance).
...
Wikipedia
