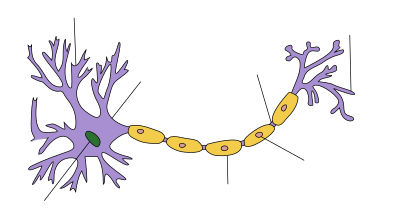
Nerve cell
| Neuron | |
|---|---|

Drawing of neurons in the pigeon cerebellum, by Spanish neuroscientist Santiago Ramón y Cajal in 1899. (A) denotes Purkinje cells and (B) denotes granule cells, both of which are multipolar.
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D009474 |
| NeuroLex ID | sao1417703748 |
| TA | A14.0.00.002 |
| TH | H2.00.06.1.00002 |
| FMA | 56566 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
| Neuron (peripheral nervous system) |
|---|
A neuron (/ˈnjʊərɒn/ NYEWR-on or /ˈnʊərɒn/ NEWR-on, also known as a neurone or nerve cell) is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals. These signals between neurons occur via specialized connections called synapses. Neurons can connect to each other to form neural networks. Neurons are major components of the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS), and of the autonomic ganglia of the peripheral nervous system.
There are several types of specialized neurons. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound or light and all other stimuli affecting the cells of the sensory organs that then send signals to the spinal cord and brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to cause muscle contractions and affect glandular outputs. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain, or spinal cord in neural networks.
...
Wikipedia