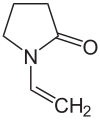
N-Vinylpyrrolidone
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
1-Ethenylpyrrolidin-2-one
|
|||
| Other names
1-Vinylpyrrolidin-2-one
1-Ethenyl-2-pyrrolidone N-Ethenyl-2-pyrrolidone N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone N-Vinylbutyrolactam |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.637 | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C6H9NO | |||
| Molar mass | 111.14 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.04 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 13–14 °C (55–57 °F; 286–287 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 92–95 °C (198–203 °F; 365–368 K) 11 mmHg | ||
| Vapor pressure | 0.1 mmHg (24 °C) | ||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.512 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 95 °C (203 °F; 368 K) | ||
| 685 °C (1,265 °F; 958 K) | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
N-Vinylpyrrolidone ("NVP") is an organic compound consisting of a 5-membered lactam linked to a vinyl group. It is a colorless liquid although commercial samples can appear yellowish.
It is produced industrially by reacting 2-pyrrolidone with acetylene. It is the precursor to polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), an important synthetic material. The NVP monomer is commonly used as a reactive diluent in ultraviolet and electron-beam curable polymers applied as inks, coatings or adhesives.
...
Wikipedia