Muscle tissue
| Muscle tissue | |
|---|---|

The body contains three types of muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle, (b) smooth muscle, and (c) cardiac muscle. (Same magnification)
|
|
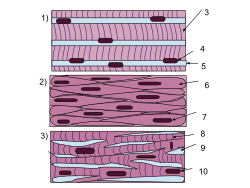
A schematic diagram of the different types of muscle cells (same order as above).
|
|
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. This is opposed to other components or tissues in muscle such as tendons or perimysium. It is formed during embryonic development through a process known as myogenesis.
Muscle tissue varies with function and location in the body. In mammals the three types are: skeletal or striated muscle; smooth or non-striated muscle; and cardiac muscle, which is sometimes known as semi-striated. Smooth and cardiac muscle contracts involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through interaction of the central nervous system as well as by receiving innervation from peripheral plexus or endocrine (hormonal) activation. Striated or skeletal muscle only contracts voluntarily, upon influence of the central nervous system. Reflexes are a form of non-conscious activation of skeletal muscles, but nonetheless arise through activation of the central nervous system, albeit not engaging cortical structures until after the contraction has occurred.
The different muscle types vary in their response to neurotransmitters and endocrine substances such as acetyl-choline, noradrenalin, adrenalin, nitric oxide and among others depending on muscle type and the exact location of the muscle.
Sub-categorization of muscle tissue is also possible, depending on among other things the content of myoglobin, , myosin ATPase etc.
...
Wikipedia
