Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | |
|---|---|
 |
|
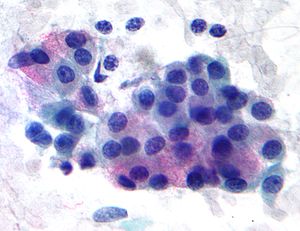
| Micrograph of a mucoepidermoid carcinoma. FNA specimen. Pap stain. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-O | M8430/3 |
| OMIM | 607536 |
| MeSH | C04.557.470.200.025.340 |
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the most common type of salivary gland malignancy in adults. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma can also be found in other organs, such as bronchi, lacrimal sac and thyroid.
Mucicarmine staining is one stain used by pathologist for detection.
Occurs in adults, with peak incidence from 20–40 years of age. A causal link with cytomegalovirus (CMV) has been strongly implicated in a 2011 research.
Presents as painless, slow-growing mass that is firm or hard. Most appear clinically as mixed tumors.
This tumor is not encapsulated and is characterized by squamous cells, mucus-secreting cells, and intermediate cells.
Mucoepidermoid carcinomas of the salivary and bronchial glands are characterized by a recurrent t(11;19)(q21;p13) chromosomal translocation resulting in a MECT1-MAML2 fusion gene. The CREB-binding domain of the CREB coactivator MECT1 (also known as CRTC1, TORC1 or WAMTP1) is fused to the transactivation domain of the Notch coactivator MAML2 PMID 16444749.
A possible association with papillomavirus has been reported.
Generally, there is a good prognosis for low-grade tumors, and a poor prognosis for high-grade tumors.
Histopathologic image of mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the major salivary gland. H & E stain
Histopathologic image of mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the major salivary gland. The same lesion as shown in a filename "Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (2) HE stain.jpg". H & E stain
Histopathologic image of mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Postoperative recurrence of the submandibular tumor. Alcian blue-PAS stain
...
Wikipedia
