Mouth (human)
| Mouth | |
|---|---|
Head and neck
|
|

A closed human mouth
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | os, cavitas oralis |
| MeSH | A01.456.505.631 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
12220513 |
| TA | A01.1.00.010 |
| FMA | 49184 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
In human anatomy, the mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and produces saliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth.
In addition to its primary role as the beginning of the digestive system, in humans the mouth also plays a significant role in communication. While primary aspects of the voice are produced in the throat, the tongue, lips, and jaw are also needed to produce the range of sounds included in human language.
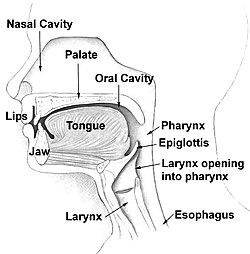
The mouth consists of two regions, the vestibule and the oral cavity proper. The mouth, normally moist, is lined with a mucous membrane, and contains the teeth. The lips mark the transition from mucous membrane to skin, which covers most of the body.
The mouth, consists of 2 regions, the vestibule and the oral cavity proper. The vestibule is the area between the teeth, lips and cheeks. The oral cavity is bounded at the sides and in front by the alveolar process (containing the teeth) and at the back by the isthmus of the fauces. Its roof is formed by hard palate and soft palate and the floor is formed by the mylohyoid muscles and is occupied mainly by the tongue. A mucous membrane – the oral mucosa, lines the sides and under surface of the tongue to the gums, lining the inner aspect of the jawbone (mandible). It receives the secretions from the submaxillary and sublingual salivary glands.
...
Wikipedia
