Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary
| Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary | |
|---|---|

Big Sur coastline looking north to Bixby Canyon Bridge. Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary.
|
|
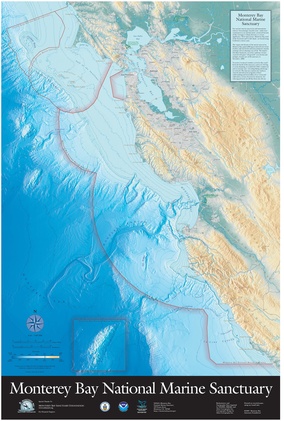
Map of the sanctuary
|
|
| Location | California's central coast, United States |
| Coordinates | 36°48′N 122°30′W / 36.8°N 122.5°WCoordinates: 36°48′N 122°30′W / 36.8°N 122.5°W |
| Area | 6,094 sq mi (15,780 km2) |
| Established | 1992 |
| Governing body | NOAA National Ocean Service |
| montereybay |
|
The Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary (MBNMS) is a US Federally protected marine area offshore of California's central coast. It is the largest US national marine sanctuary and has a shoreline length of 276 miles (444 km) stretching from just north of the Golden Gate Bridge at San Francisco to Cambria in San Luis Obispo County. Supporting one of the world’s most diverse marine ecosystems, it is home to numerous mammals, seabirds, fishes, invertebrates and plants in a remarkably productive coastal environment. The MBNMS was established in 1992 for the purpose of resource protection, research, education, and public use.
The Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary (MBNMS) is one of the largest of a system of 13 National Marine Sanctuaries administered by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), within the U.S. Department of Commerce. It stretches from Rocky Point in Marin County, just north of the Golden Gate Bridge, to the town of Cambria in San Luis Obispo County, and encompasses a shoreline length of 276 miles (444 km) and 6,094 square miles (15,783 km2) of ocean surrounding Monterey Bay. Its seaward Boundary is an average of 30 miles (48 km) offshore, and shoreward boundary the mean high tide. Its area is 6,094 square statute miles or 4,024 square nautical miles. The deepest point is 10,663 feet (3,250 meters) in the Monterey Submarine Canyon, which is deeper than the Grand Canyon. The average ocean surface temperature is 55 °F (13 °C).
...
Wikipedia
