Mole (skin)
| Melanocytic nevus | |
|---|---|
 |
|
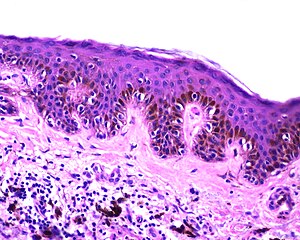
| Lentiginous melanocytic naevus | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| ICD-10 | D22 |
| ICD-9-CM | 216 |
| DiseasesDB | 8333 |
| eMedicine | derm/289 |
| MeSH | D009508 |
A melanocytic nevus (also known as "nevocytic nevus" or "nevus-cell nevus") is a type of lesion that contains nevus cells (a type of melanocyte). Some sources equate the term mole with "melanocytic nevus". Other sources reserve the term "mole" for other purposes.
The majority of moles appear during the first two decades of a person's life, with about one in every 100 babies being born with moles. Acquired moles are a form of benign neoplasm, while congenital moles, or congenital nevi, are considered a minor malformation or hamartoma and may be at a higher risk for melanoma. A mole can be either subdermal (under the skin) or a pigmented growth on the skin, formed mostly of a type of cell known as a melanocyte. The high concentration of the body's pigmenting agent, melanin, is responsible for their dark color. Moles are a member of the family of skin lesions known as nevi.
Some sources equate the term mole with "melanocytic nevus". Other sources reserve the term "mole" for other purposes such as the animal of the same name. Melanocytic nevi represent a family of lesions. The most common variants are:
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, the most common types of moles are skin tags, raised moles and flat moles. Benign moles are usually brown, tan, pink or black (especially on dark-colored skin). They are circular or oval and are usually small (commonly between 1–3 mm), though some can be larger than the size of a typical pencil eraser (>5 mm). Some moles produce dark, coarse hair. Common mole hair removal procedures include plucking, cosmetic waxing, electrolysis, threading and cauterization.
...
Wikipedia
