Minimally conscious state
| Minimally Conscious State | |
|---|---|
 |
|
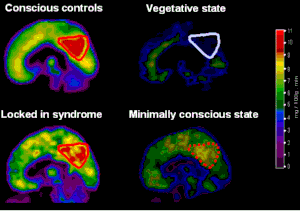
| Brain scans of various disorders of consciousness, including minimally conscious state | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| MeSH | D018458 |
A minimally conscious state (MCS) is a disorder of consciousness distinct from persistent vegetative state and locked-in syndrome. Unlike persistent vegetative state, patients with MCS have partial preservation of conscious awareness. MCS is a relatively new category of disorders of consciousness. The natural history and longer term outcome of MCS have not yet been thoroughly studied. The prevalence of MCS was estimated to be 112,000 to 280,000 in adult and pediatric cases.
Prior to the mid-1990s, there was a lack of operational definitions available to clinicians and researchers to guide the differential diagnosis among disorders of consciousness. As a result, patients were lumped together into broad categories often based on the severity of the disability (e.g. moderate, severe, extremely severe). These diagnoses were performed without regard to salient differences in behavioral and pathological characteristics. In a three-year period spanning from 1994–1996, three position statements regarding the diagnostic criteria of disorder of consciousness were published. The “Medical Aspects of the Persistent Vegetative State” was published by the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) in 1994. In 1995, “Recommendations for Use of Uniform Nomenclature Pertinent to Patients With Severe Alterations in Consciousness” was published by the American Congress of Rehabilitation Medicine (ACRM). In 1996 the “International Working Party on the Management of the Vegetative State: Summary Report” was published by a group of international delegates from neurology, rehabilitation, neurosurgery, and neuropsychology. However, because the diagnostic criteria were published independently from one another, the final recommendations differed greatly from one another. The Aspen Neurobehavioral Work-group was convened to explore the underlying causes of these disparities. In the end, the Aspen Work-group provided a consensus statement regarding definitions and diagnostic criteria disorder of consciousness which include the vegetative state (VS) and the minimally conscious state (MCS).
...
Wikipedia
