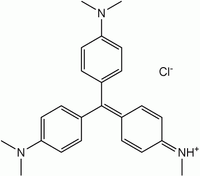
Methyl violet
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Methyl violet 2B
|
|
| Other names
Gentian violet B,
Methylrosanilinium chloride, |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
8004-87-3 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL64894 |
| ChemSpider |
170606 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.111.727 |
| PubChem | 196986 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C24H28N3Cl | |
| Appearance | Green to dark-green powder |
| Melting point | 137 °C (279 °F; 410 K) decomposes |
| Soluble in water, ethanol, insoluble in xylene | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Methylrosanilinium chloride,
Hexamethylparosanilinium chloride,
Basic Violet 3,
Methyl violet is a family of organic compounds that are mainly used as dyes. Depending on the number of attached methyl groups, the color of the dye can be altered. Its main use is as a purple dye for textiles and to give deep violet colors in paint and ink. Methyl violet 10B is also known as crystal violet (and many other names) and has medical uses.
The term methyl violet encompasses three compounds that differ in the number of methyl groups attached to the amine functional group. They are all soluble in water, ethanol, diethylene glycol and dipropylene glycol.
Methyl violet 2B (IUPAC name: N-(4-(bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)methylene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)methanaminium chloride) is a green powder which is soluble in water in ethanol and water, but not in xylene. It appears yellow in solution of low pH (~0.15) and changes to violet with pH increasing toward 3.2.
Methyl violet 10B has six methyl groups. It is known in medicine as Gentian violet (or crystal violet or pyoctanin(e)) and is the active ingredient in a Gram stain, used to classify bacteria. It is used as a pH indicator, with a range between 0 and 1.6. The protonated form (found in acidic conditions) is yellow, turning blue-violet above pH levels of 1.6. Gentian violet destroys cells and can be used as a disinfectant. Compounds related to methyl violet are potential carcinogens.
Methyl violet 10B inhibits the growth of many Gram positive bacteria, except . When used in conjunction with nalidixic acid (which destroys gram-negative bacteria), it can be used to isolate the streptococci bacteria for the diagnosis of an infection.
...
Wikipedia
