Methyl alcohol poisoning
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈmɛθənɒl/ | ||
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Methanol
|
|||
| Other names
Carbinol
Columbian spirits Hydroxymethane Methyl alcohol Methyl hydrate Methyl hydroxide Methylic alcohol Methylol Pyroligneous spirit Wood alcohol Wood naphtha Wood spirit |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | B01170 | ||
| 1098229 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.599 | ||
| EC Number | 200-659-6 | ||
| 449 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Methanol | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | PC1400000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1230 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
|
CH 3OH or CH 4O |
|||
| Molar mass | 32.04 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.792 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −97.6 °C (−143.7 °F; 175.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 64.7 °C (148.5 °F; 337.8 K) | ||
| miscible | |||
| log P | −0.69 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 13.02 kPa (at 20 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 15.5 | ||
| −21.40·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.33141 | ||
| Viscosity | 0.545 mPa·s (at 25 °C) | ||
| 1.69 D | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | See: data page | ||
| GHS pictograms |
  
|
||
| GHS signal word | Danger | ||
| H225, H301, H311, H331, H370 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+310, P303+361+353, P304+340, P330, P363, P370+378, P403+233, P235, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | 11 to 12 °C (52 to 54 °F; 284 to 285 K) | ||
| 470 °C (878 °F; 743 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 6–36% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
5628 mg/kg (rat, oral) 7300 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 12880 mg/kg (rat, oral) 14200 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) |
||
|
LC50 (median concentration)
|
64,000 ppm (rat, 4 h) | ||
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
33,082 ppm (cat, 6 h) 37,594 ppm (mouse, 2 h) |
||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 200 ppm (260 mg/m3) | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 200 ppm (260 mg/m3) ST 250 ppm (325 mg/m3) [skin] | ||
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
6000 ppm | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related compounds
|
Methanethiol Silanol |
||
| Supplementary data page | |||
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
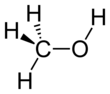
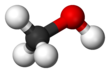
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol among others, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH (often abbreviated MeOH). Methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly as a byproduct of the destructive distillation of wood. Today, industrial methanol is produced in a catalytic process directly from carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen.
Methanol is the simplest alcohol, being only a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group. It is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to that of ethanol (drinking alcohol). However, unlike ethanol, methanol is highly toxic and unfit for consumption. At room temperature, it is a polar liquid. It is used as an antifreeze, solvent, fuel, and as a denaturant for ethanol. It is also used for producing biodiesel by transesterification reaction.
Methanol is produced naturally in the anaerobic metabolism of many varieties of bacteria and is commonly present in small amounts in the environment. As a result, the atmosphere contains a small amount of methanol vapor. However, in only a few days, atmospheric methanol is oxidized by sunlight to produce carbon dioxide and water.
...
Wikipedia