MetNet
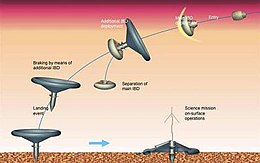
Mars MetNet impactor concept
|
|
| Mission type | Technology Atmospheric science |
|---|---|
| Operator | Finnish Meteorological Institute |
| Website | http://fmispace.fmi.fi/index.php?id=metnet |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Landing mass | entry mass: 22.2 kg per unit |
| Payload mass | 4 kg allocation |
| Dimensions | Impactor: 1.8 m diameter |
| Power | 0.6 W |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | TBD |
| Rocket | TBD |
| Mars impactor | |
Mars MetNet is a planned atmospheric science mission to Mars, initiated by the Finnish Meteorological Institute (FMI) and under development by Finland, Russia and Spain. By September 2013, two flight-capable entry, descent and landing systems (EDLS) have been manufactured and tested. As of 2015 baseline funding exists until 2020. As of 2016 launch vehicle or precursory launch date has not been set.
The objective is to establish a widespread surface observation network on Mars to investigate the planet's atmospheric structure, physics and meteorology. The bulk of the mission consist of at least 16 MetNet impact landers deployed over the Martian surface.
The basic concepts of Mars MetNet were initiated by the Finnish Meteorological Institute (FMI) team in late 1980s. The concept was matured over a decade, and eventually the development work started in the year 2000. MetNet can be considered as a successor of the NetLander, Russian Mars 96 and the earlier ESA Marsnet and InterMarsnet mission concepts. Of these Mars 96 went all the way to launch, but failure on the trans-mars injection with forth stage of the rocket caused it to re-enter Earth and break-up. As part of this multi-part mission were two penetrators quite like MetNet. Main difference being that on the impact the front part would separate from the back and delve some meters deeper into groud.
MetNet was among the missions proposed at the European Geosciences Union General Assembly in April 2016.
The scope of the Mars MetNet mission is eventually to deploy several tens of impact landers on the Martian surface. Mars MetNet is being developed by a consortium consisting of the Finnish Meteorological Institute (Mission Lead), the Russian Space Research Institute (IKI) (in cooperation with Lavochkin Association), and Instituto Nacional de Técnica Aeroespacial (INTA) from Spain.
...
Wikipedia
