Mannitol
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Osmitrol, other |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
intravenous by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~7% |
| Metabolism | Liver, negligible |
| Biological half-life | 100 minutes |
| Excretion | Kidney: 90% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | D-Mannitol, mannite, manna sugar |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | E421 (thickeners, ...) |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.647 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
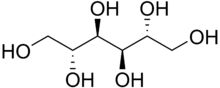
| Formula | C6H14O6 |
| Molar mass | 182.172 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Mannitol is a type of sugar which is also used as a medication. As a sugar, it is often used as a sweetener in diabetic food, as it is poorly absorbed from the intestines. As a medication, it is used to decrease high pressures in the eyes such as are seen in glaucoma and to lower increased intracranial pressure. Medically, it is given by injection. Effects typically begin within 15 minutes and last up to 8 hours.
Common side effects from medical use include electrolyte problems and dehydration. Other serious side effects may include worsening heart failure and kidney problems. It is unclear if use is safe in pregnancy. Mannitol is in the osmotic diuretic family of medications and works by pulling fluid from the brain and eyes.
The discovery of mannitol is attributed to Joseph Louis Proust in 1806. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. The wholesale cost in the developing world is about US$1.12 to 5.80 a dose. In the United States, a course of treatment costs $25 to 50. It was originally made from the flowering ash and called manna after its supposed resemblance to the Biblical food.
Mannitol is used to reduce acutely raised intracranial pressure until more definitive treatment can be applied, e.g., after head trauma.
...
Wikipedia
