Male urethra
| Urethra | |
|---|---|
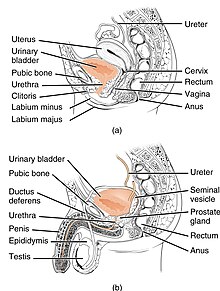
The urethra transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. This image shows (a) a female urethra and (b) a male urethra.
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | Urogenital sinus |
| Artery |
Inferior vesical artery Middle rectal artery Internal pudendal artery |
| Vein |
Inferior vesical vein Middle rectal vein Internal pudendal vein |
| Nerve |
Pudendal nerve Pelvic splanchnic nerves Inferior hypogastric plexus |
| Lymph |
Internal iliac lymph nodes Deep inguinal lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | urethra vagina; feminina (female); urethra masculina (male) |
| Greek | οὐρήθρα |
| MeSH | A05.360.444.492.726 |
| TA |
A08.4.01.001F A08.5.01.001M |
| FMA | 19667 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
In anatomy, the urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ourḗthrā) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of fluids from the body. In male placental mammals, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine. In female placental mammals, the urethra is shorter and emerges at the female external urethral orifice above the vaginal opening.
Female placental mammals use their urethra only for urinating, but male placental mammals use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination.
In the human female, the urethra is about 1.9 inches (4.8 cm) to 2 inches (5.1 cm) long and exits the body between the clitoris and the vagina, extending from the internal to the external urethral orifice. The meatus is located below the clitoris. It is placed behind the symphysis pubis, embedded in the anterior wall of the vagina, and its direction is obliquely downward and forward; it is slightly curved with the concavity directed forward. The proximal 2/3rds is lined by transitional epithelium cells while distal 1/3rd is lined by stratified squamous epithelium cells.
The urethra consists of three coats: muscular, erectile, and mucous, the muscular layer being a continuation of that of the bladder. Between the superior and inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm, the female urethra is surrounded by the urethral sphincter. Somatic (conscious) innervation of the external urethral sphincter is supplied by the pudendal nerve. The uro-genital sinus may be divided into three component parts. The first of these is the cranial portion which is continuous with the allantois and forms the bladder proper. The pelvic part of the sinus forms the prostatic urethra and epithelium as well as the membranous urethra and bulbo urethral glands in the male and the membranous urethra and part of the vagina in females.
...
Wikipedia
