Lyrica
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /priˈɡæbəlᵻn/ |
| Trade names | Lyrica, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605045 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Dependence liability |
Physical: Moderate Psychological: Moderate |
| Addiction liability |
Low |
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code | N03AX16 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | High (≥90% rapidly absorbed; administration with food has no significant effect on bioavailability) |
| Protein binding | Nil |
| Metabolites | N-methylpregabalin |
| Onset of action | may occur within a week (pain) |
| Biological half-life | 6.3 to 11.5 hours |
| Duration of action | Unknown |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | 3-isobutyl GABA |
| CAS Number |
148553-50-8 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5486971 |
| DrugBank |
DB00230 |
| ChemSpider |
4589156 |
| UNII |
55JG375S6M |
| KEGG |
D02716 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:64356 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1059 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.119.513 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
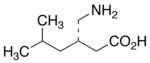
| Formula | C8H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 159.23 g.mol−1 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Pregabalin, marketed under the brand name Lyrica among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and generalized anxiety disorder. Its use for epilepsy is as an add-on therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization in adults. Some off-label uses of pregabalin include restless leg syndrome, prevention of migraines,social anxiety disorder, and alcohol withdrawal. When used before surgery it does not appear to affect pain after surgery but may decrease the use of opioids.
Common side effects include: sleepiness, confusion, trouble with memory, poor motor coordination, dry mouth, problem with vision, and weight gain. Potentially serious side effects include angioedema, drug misuse, and an increased suicide risk. When pregabalin is taken at high doses over a long period of time, addiction may occur, but if taken at usual doses the risk of addiction is low. It is classified as a GABA analogue.
Parke-Davis developed pregabalin as a successor to gabapentin and was brought to market by Pfizer after the company acquired Warner-Lambert. There is to be no generic version available in the United States until 2018. A generic version is available in Canada and the United Kingdom. In the US it costs about 300-400 USD per month. Pregabalin is a Schedule V controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970 (CSA).
...
Wikipedia
