Lymphoblastic lymphoma
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Hematology and oncology |
| ICD-10 | C91.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 204.0 |
| ICD-O | M9835/3 |
| DiseasesDB | 195 |
| eMedicine | med/3146 ped/2587 |
| MeSH | D054198 |
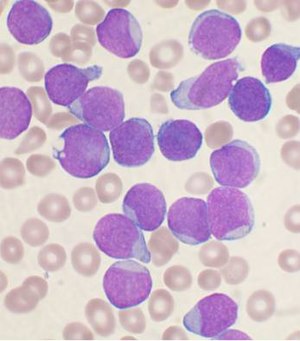
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, also known as acute lymphocytic leukemia or acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL), is an acute form of leukemia, or cancer of the white blood cells, characterized by the overproduction and accumulation of cancerous, immature white blood cells, known as lymphoblasts. In persons with ALL, lymphoblasts are overproduced in the bone marrow and continuously multiply, causing damage and death by inhibiting the production of normal cells (such as red and white blood cells and platelets) in the bone marrow and by spreading (infiltrating) to other organs. ALL is most common in childhood, with a peak incidence at 2–5 years of age and another peak in old age.
The symptoms of ALL are indicative of a reduced production of functional blood cells, because leukemia wastes the resources of the bone marrow that are normally used to produce new, functioning blood cells. These symptoms can include fever, increased risk of infection (especially bacterial infections like pneumonia, due to neutropenia; symptoms of such an infection include shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, vomiting, changes in bowel or bladder habits), increased tendency to bleed (due to thrombocytopenia), and signs indicative of anemia, including pallor, tachycardia (high heart rate), fatigue, and headache.
About 6,000 cases are reported in the United States every year. Internationally, ALL is more common in Caucasians than in Africans; it is more common in Hispanics and in Latin America. Cure is a realistic goal and is achieved in more than 80% of affected children, although only 20-40% of adults are cured. "Acute" is defined by the World Health organization standards, in which greater than 20% of the cells in the bone marrow are blasts. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is defined as having less than 20% blasts in the bone marrow.
...
Wikipedia
