Lunokhod 2
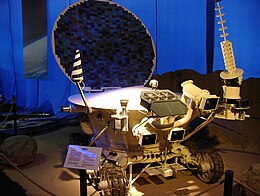
Lunokhod 2 rover
|
|
| Mission type | Lunar rover |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1973-001A |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Dry mass | 840 kilograms (1,850 lb) (rover only) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 11 January 1973, 06:55:38 UTC |
| Rocket | Proton-K/D |
| Launch site | Baikonur 81/23 |
| End of mission | |
| Last contact | 11 May 1973 |
| Lunar rover | |
| Spacecraft component | Rover |
| Landing date | 15 January 1973 |
Lunokhod 2 (Russian: Луноход-2, moon walker) was the second of two unmanned lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of the Lunokhod programme.
The Luna 21 spacecraft landed on the Moon and deployed the second Soviet lunar rover (Lunokhod 2) in January 1973. The primary objectives of the mission were to collect images of the lunar surface, examine ambient light levels to determine the feasibility of astronomical observations from the Moon, perform laser ranging experiments from Earth, observe solar X-rays, measure local magnetic fields, and study the soil mechanics of the lunar surface material.
The rover stood 135 cm (4 ft 5 in) high and had a mass of 840 kg (1,850 lb). It was about 170 cm (5 ft 7 in) long and 160 cm (5 ft 3 in) wide and had eight wheels each with an independent suspension, electric motor and brake. The rover had two speeds, ~1 km/h and ~2 km/h (0.6 mph and 1.2 mph). Lunokhod 2 was equipped with three television cameras, one mounted high on the rover for navigation, which could return high resolution images at different frame rates—3.2, 5.7, 10.9 or 21.1 seconds per frame. These images were used by a five-man team of controllers on Earth who sent driving commands to the rover in real time. Power was supplied by a solar panel on the inside of a round hinged lid which covered the instrument bay, which would charge the batteries when opened. A polonium-210 radioisotope heater unit was used to keep the rover warm during the long lunar nights. There were four panoramic cameras mounted on the rover. Scientific instruments included a soil mechanics tester, solar X-ray experiment, an astrophotometer to measure visible and ultraviolet light levels, a magnetometer deployed in front of the rover on the end of a 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) boom, a radiometer, a photodetector (Rubin-1) for laser detection experiments, and a French-supplied laser corner reflector. The lander carried a bas relief of Vladimir Lenin and the Soviet coat of arms. The lander and rover together massed 1814 kg.
...
Wikipedia
