Lowland streaked tenrec
| Lowland streaked tenrec | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Afrosoricida |
| Family: | Tenrecidae |
| Genus: | Hemicentetes |
| Species: | H. semispinosus |
| Binomial name | |
|
Hemicentetes semispinosus G. Cuvier, 1798 |
|
 |
|
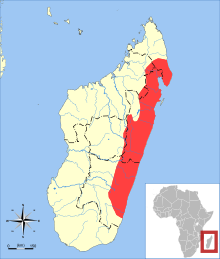
| Lowland streaked tenrec range | |
The lowland streaked tenrec (Hemicentetes semispinosus) is a small tenrec found in Madagascar.
The species is found in tropical lowland rain forest, in the northern and eastern parts of Madagascar.
It is a small animal, with a long snout and limbs, and a vestigial tail. Pelage black with yellow longitudinal stripes dorsally, light beneath; scattered quills, some barbed and detachable.
The head and body are 12.2–16.5 cm (4.8–6.5 in) in length. The weight is about 200 grams (7 oz).
It is active during day and night, primarily feeding on insects. Most tenrecs possess a long snout for poking around in the ground to find their food. They are also capable of eating worms and fruits. Some species of tenrecs live in water and eat small fish and even frogs.
Breeding takes place during October to December and possibly at other times, depending upon local food supply and temperature. The gestation period lasts 58 days, and the female gives birth to usually between 5 and 8 young. The young are weaned at 18 to 25 days.
The streaked tenrec lives in long, shallow burrows which are usually occupied by family groups.
If threatened by a predator (most commonly a fossa or Malagasy mongoose), a streaked tenrec erects the barbed quills on its back and on the crest around its head, pointing them completely forward, and drives them in to the attacker's nose or paws with body and head movements. The unbarbed quills are clustered in the middle of the back, and produce a faint chattering sound when vibrated, and are used to communicate within family groups.
The streaked tenrec is the only mammal known to use stridulation for generating sound, a method more commonly associated with insects and snakes.
...
Wikipedia

