Lowell canal system
|
Lowell Locks and Canals Historic District
|
|
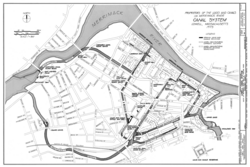
A 1975 map showing the canal system
|
|
| Location | Lowell, Massachusetts |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 42°38′44″N 71°19′12″W / 42.64556°N 71.32000°WCoordinates: 42°38′44″N 71°19′12″W / 42.64556°N 71.32000°W |
| Built | 1821 |
| Architect | Nathan Appleton, Kirk Boott |
| NRHP reference # | 76001972 |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | August 13, 1976 |
| Designated NHLD | December 22, 1977 |
The Lowell Power Canal System is the largest power canal system in the United States, at 5.6 miles in length. The system's estimated output is 10,000 horsepower, operating six major canals on two levels, controlled by numerous gates. The system was begun in the 1790s, beginning its life as a transportation canal called the Pawtucket Canal, which was constructed to get logs from New Hampshire down the Merrimack River to shipbuilding centers at Newburyport, Massachusetts, bypassing the 30-plus-foot drop of the Pawtucket Falls.
In the early 1820s, Associates of the recently deceased Francis Cabot Lowell bought up the old Pawtucket Canal in what was then East Chelmsford, Massachusetts. Within a few years, the new industrial center that became Lowell was using canals feeding off of a widened and deepened Pawtucket Canal as a direct power source for their textile mills. The first of these canals was the Merrimack Canal, which powered the Merrimack Manufacturing Company. The repurposing of the Proprietors of Locks and Canals allowed the Associates to sell water power to other companies, starting with the Hamilton Canal, leading to the explosive growth of the town, and then shortly thereafter, city, of Lowell.
By the late 1840s, Lowell's canal system was producing as much power as possible. However, the Chief Engineer of Locks and Canals, an Englishman by the name of James B. Francis devised the Northern Canal and the Moody Street Feeder, to increase the capacity of, and availability of water to various parts of, the whole system. The Pawtucket Gatehouse was constructed to control flow from behind the Pawtucket Dam into the Northern Canal.
The dam itself, which was built twenty years earlier, was lengthened at that time, diverting the entire Merrimack (during periods of lower flow) into the two canal system entrances above it. It is a stone dam topped with wooden flashboards – a system still used on this dam today. The level of the water is regulated by the flashboards and the metal pins that hold them back. When there is too much water going over the top of the dam, the pins bend backwards, releasing the boards, and the outflow of the dam is increased.
...
Wikipedia


