Lilial
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
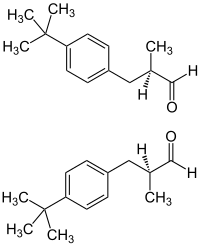
3-(4-tert-Butylphenyl)-2-methylpropanal
|
|
Other names
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.173 |
| EC Number | 201-289-8 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | MW4895000 |
| UN number | 3082 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C14H20O | |
| Molar mass | 204.31 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | clear viscous liquid |
| Density | 0.94 g/ml |
| Melting point | −20 °C (−4 °F; 253 K) |
| Boiling point | 275 °C (527 °F; 548 K) |
| 0.045 g/l at 20 °C | |
| log P | 4.36 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Topical | |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related aldehydes
|
Bourgeonal |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Isobutyraldehyde
Hexyl cinnamaldehyde
2-Methylundecanal
Lilial (a trade name for lily aldehyde, also known as lysmeral) is a chemical compound commonly used as a perfume in cosmetic preparations and laundry powders, often under the name butylphenyl methylpropional. It is a synthetic aromatic aldehyde.
Lilial may be prepared via a number of routes but is typically produced via a crossed-aldol condensation between para-tert-butylbenzaldehyde and propanal, followed by hydrogenation of the intermediate alkene. This produces a racemic product.
Lilial is commonly produced and sold as a racemic mixture, however testing has indicated that the different enantiomers of the compound do not contribute equally to its odor. The R-enantiomer has a strong floral odor, reminiscent of cyclamen or lily of the valley; whereas the S-enantiomer possesses no strong odor.
Like most aldehydes Lilial is not long term stable and tends to slowly oxidize on storage.
It can sometimes act as an allergen and may cause contact dermatitis in susceptible individuals.
...
Wikipedia
