Levoamphetamine
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
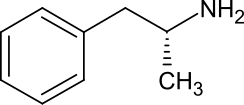
(2R)-1-Phenylpropan-2-amine
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
156-34-3 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) |
Interactive image Interactive image |
| 2432739 | |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:42724 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL19393 |
| ChemSpider |
30477 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.320 |
| EC Number | 205-850-8 |
| 1125855 | |
| 2146 | |
| PubChem | 32893 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H13N | |
| Molar mass | 135.2062 g mol−1 |
| log P | 1.789 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Oral (as part of Adderall, Evekeo, and generic amphetamine sulfate) | |
| Legal status |
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Levoamphetamine, also known as levamfetamine (INN),(R)-amphetamine,(−)-amphetamine, and L-amphetamine, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant known to increase wakefulness and concentration in association with decreased appetite and fatigue. Pharmaceuticals that contain levoamphetamine are currently indicated and prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obesity, and narcolepsy in some countries.
Levoamphetamine is the levorotatory stereoisomer of the amphetamine molecule.
Levoamphetamine is the levorotary stereoisomer of the amphetamine molecule. Racemic amphetamine contains two optical isomers, dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine.
The first patented amphetamine brand, Benzedrine, was a racemic (i.e., equal parts) mixture of the freebases or sulfate salts of both amphetamine enantiomers (levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine) that was introduced in the United States in 1934 as an inhaler for treating nasal congestion. It was later realized that the amphetamine enantiomers could treat obesity, narcolepsy, and ADHD. Because of the greater central nervous system effect of the dextro enantiomer, sold as Dexedrine, prescription of the Benzedrine brand fell and was eventually discontinued. However, in 2012 racemic amphetamine sulfate was reintroduced as the Evekeo brandname.
...
Wikipedia
