Lateral medullary syndrome
| Lateral medullary syndrome | |
|---|---|
 |
|
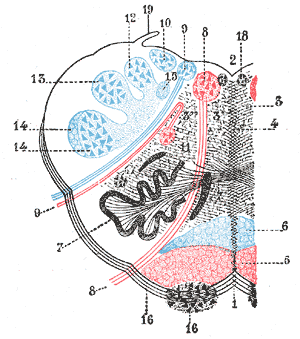
| Medulla oblongata, shown by a transverse section passing through the middle of the olive. (Lateral medullary syndrome can affect structures in upper left: #9=vagus nerve, #10=acoustic nucleus, #12=nucleus gracilis, #13=nucleus cuneatus, #14=head of posterior column and lower sensory root of trigeminal nerve and #19=Ligula.) | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | neurology |
| ICD-10 | G46.4 |
| DiseasesDB | 10449 |
| eMedicine | emerg/834 |
| MeSH | D014854 |
Lateral medullary syndrome (also called Wallenberg syndrome and posterior inferior cerebellar artery syndrome) is a neurological disorder causing a range of symptoms due to ischemia in the lateral part of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. The ischemia is a result of a blockage in the posterior inferior cerebellar artery or one of its branches.
This syndrome is characterized by sensory deficits affecting the trunk (torso) and extremities on the opposite side of the infarction and sensory deficits affecting the face and cranial nerves on the same side with the infarct. Specifically, there is a loss of pain and temperature sensation on the contralateral (opposite) side of the body and ipsilateral (same) side of the face. This crossed finding is diagnostic for the syndrome.
Clinical symptoms include swallowing difficulty, or dysphagia, slurred speech, ataxia, facial pain, vertigo, nystagmus, Horner's syndrome, diplopia, and possibly palatal myoclonus.
Affected persons have difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia) resulting from involvement of the nucleus ambiguus, as well as slurred speech (dysarthria) and disordered vocal quality (dysphonia) . Damage to the spinal trigeminal nucleus causes absence of pain on the ipsilateral side of the face, as well as an absent corneal reflex.
The spinothalamic tract is damaged, resulting in loss of pain and temperature sensation on the opposite side of the body. The damage to the cerebellum or the inferior cerebellar peduncle can cause ataxia. Damage to the hypothalamospinal fibers disrupts sympathetic nervous system relay and gives symptoms analogous to Horner syndrome.
...
Wikipedia
