Laparotomy
| Laparotomy | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | |
|
|
| ICD-9-CM | 54.1 |
| MeSH | D007813 |
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a large incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as a celiotomy. The first successful laparotomy was performed without anesthesia by Ephraim McDowell in 1809 in Danville, Kentucky.
The term arises from the Greek word "lapara," meaning "flank," and the suffix "-tomy" arising from the Greek word "τομή" meaning "a (surgical) cut."
In diagnostic laparotomy (most often referred to as an exploratory laparotomy and abbreviated ex-lap), the nature of the disease is unknown, and laparotomy is deemed the best way to identify the cause.
In therapeutic laparotomy, a cause has been identified (e.g. colon cancer) and the operation is required for its therapy.
Usually, only exploratory laparotomy is considered a stand-alone surgical operation. When a specific operation is already planned, laparotomy is considered merely the first step of the procedure.
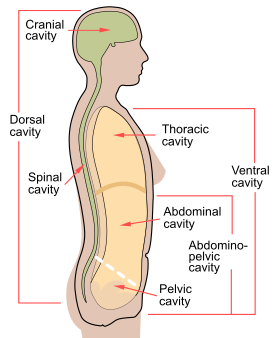
Depending on incision placement, laparotomy may give access to any abdominal organ or space, and is the first step in any major diagnostic or therapeutic surgical procedure of these organs, which include:
The most common incision for laparotomy is the midline incision, a vertical incision which follows the linea alba.
Midline incisions are particularly favoured in diagnostic laparotomy, as they allow wide access to most of the abdominal cavity.
Other common laparotomy incisions include:
A related procedure is laparoscopy, where cameras and other instruments are inserted into the peritoneal cavity via small holes in the abdomen. For example, an appendectomy can be done either by a laparotomy or by a laparoscopic approach.
...
Wikipedia
