Lanthionine
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
|
922-55-4 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:21347 |
| ChemSpider |
88959 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.888 |
| PubChem | 256406 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H12N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 208.2318 g/mol |
| Melting point | 280 to 283 °C (536 to 541 °F; 553 to 556 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
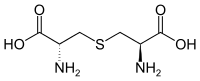
Lanthionine is a nonproteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula (HOOC-CH(NH2)-CH2-S-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH). It is a thioether dimer of cystine, composed of two alanine residues that are crosslinked on their β-carbon via a sulfur atom. Despite its name, lanthionine does not contain the element lanthanum.
In 1941, lanthionine was first isolated from the treatment of wool with sodium carbonate and was first synthesized from cysteine and β-chloroalanine. Lanthionines are found widely in nature and have been isolated from human hair, lactalbumin, and feathers. Lanthionines have also been found in bacterial cell walls and are the components of a group of gene-encoded peptide antibiotics called lantibiotics, which includes nisin (a food preservative), subtilin, epidermin (effective against staphylococcus and ), and ancovenin (an enzyme inhibitor).
A variety of syntheses of lanthionine have been published including sulfur extrusion from cystine, ring opening of serine β-lactone, and hetero-conjugate addition of cysteine to dehydroalanine. The sulfur extrusion method is, however, the only pathway for lanthionine that has been employed in the total synthesis of a lantibiotic.
...
Wikipedia
