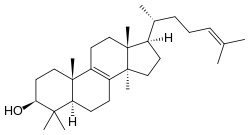
Lanosterol
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
lanosta-8,24-dien-3-ol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
79-63-0 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:16521 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL225111 |
| ChemSpider |
216175 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.105 |
| 2746 | |
| MeSH | Lanosterol |
| PubChem | 246983 |
| UNII |
1J05Z83K3M |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C30H50O | |
| Molar mass | 426.71 g/mol |
| Melting point | 138 to 140 °C (280 to 284 °F; 411 to 413 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungi steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.
Elaboration of lanosterol under enzyme catalysis leads to the core structure of steroids. 14-Demethylation of lanosterol by eventually yields cholesterol.
Recent research suggests that lanosterol might be instrumental in prevention of formation of cataracts in mammals.
Preliminary studies in dogs and rabbits have shown that lanosterol can prevent and even reverse cataract formation. However, an attempt to replicate these results in age-related cataractous human lens nuclei removed during manual small incision cataract surgery by immersing them in lanosterol solution and incubating them for 6 days according to the method of Zhao et al., failed to reverse nuclear opacity.
...
Wikipedia
