Laetrile
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
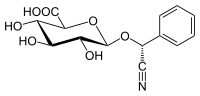
IUPAC name
[(6-O-β-D-Glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy](phenyl)acetonitrile
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.045.372 |
| MeSH | Amygdalin |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C20H27NO11 | |
| Molar mass | 457.429 |
| Melting point | 223-226 °C(lit.) |
| H2O: 0.1 g/mL hot, clear to very faintly turbid, colorless | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | A6005 |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H302 | |
| P264, P270, P301+312, P330, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Vicianin, laetrile, prunasin, sambunigrin |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-cyano(phenyl)methoxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid
|
|
| Other names
L-mandelonitrile-β-D-glucuronide, Vitamin B₁₇
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.045.372 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C14H15NO7 | |
| Molar mass | 309.2714 |
| Melting point | 214 to 216 °C (417 to 421 °F; 487 to 489 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Amygdalin (from Ancient Greek: ἀμυγδαλή amygdálē "almond") is a poisonous cyanogenic glycoside found in many plants, but most notably in the seeds (kernels) of apricot, bitter almonds, apple, peach, and plum.
Since the early 1950s, both amygdalin and a modified form named laetrile have been promoted as alternative cancer treatments, often using the misnomer Vitamin B17. But studies have found them to be clinically ineffective in the treatment of cancer, as well as potentially toxic or lethal when taken by mouth, due to cyanide poisoning. Neither amygdalin nor laetrile is a vitamin.
The promotion of laetrile to treat cancer has been described in the medical literature as a canonical example of quackery, and as "the slickest, most sophisticated, and certainly the most remunerative cancer quack promotion in medical history".
Amygdalin is a cyanogenic glycoside derived from the aromatic amino acid phenylalanine. Amygdalin and prunasin are very common among plants of the Rosaceae family, particularly the genus Prunus, Poaceae (grasses), Fabaceae (legumes), and in other food plants, including linseed and manioc. Sambunigrin, obtained from leaves of the elder tree (Sambucus nigra), is isomeric to prunasin. Within these plants, amygdalin and the enzymes necessary to hydrolyze them are stored in separate locations so that they will mix in response to tissue damage. This provides a natural defense system
...
Wikipedia

