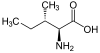
L-isoleucine
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Isoleucine
|
|||
| Other names
2-Amino-3-methylpentanoic acid
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.726 | ||
| KEGG | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C6H13NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 131.18 g·mol−1 | ||
| -84.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Isoleucine (abbreviated as Ile or I) encoded by the codons ATT, ATC, ATA is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+
3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a hydrocarbon side chain, classifying it as a non-polar, uncharged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it, and must be ingested in our diet. Isoleucine is synthesized from pyruvate employing leucine biosynthesis enzymes in other organisms such as bacteria.
Inability to break down isoleucine, along with other amino acids, is associated with the disease called Maple Syrup Urine Disease, which results in discoloration and a sweet smell in the patient's urine, which is where the name comes from. However, in severe cases, MSUD can lead to damage to the brain cells and ultimately death.
As an essential nutrient, it is not synthesized in the body, hence it must be ingested, usually as a component of proteins. In plants and microorganisms, it is synthesized via several steps, starting from pyruvic acid and alpha-ketoglutarate. Enzymes involved in this biosynthesis include:
Isoleucine is both a glucogenic and a ketogenic amino acid. After transamination with alpha-ketoglutarate the carbon skeleton can be converted into either Succinyl CoA, and fed into the TCA cycle for oxidation or converted into oxaloacetate for gluconeogenesis (hence glucogenic). It can also be converted into Acetyl CoA and fed into the TCA cycle by condensing with oxaloacetate to form citrate. In mammals Acetyl CoA cannot be converted back to carbohydrate but can be used in the synthesis of ketone bodies or fatty acids, hence ketogenic.
...
Wikipedia