L-DOPA
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
oral, intravenous |
| ATC code | N04BA01 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30% |
| Metabolism | Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase |
| Biological half-life | 0.75–1.5 hours |
| Excretion | renal 70–80% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
59-92-7 |
| PubChem (CID) | 6047 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 3639 |
| DrugBank |
DB01235 |
| ChemSpider |
5824 |
| UNII |
46627O600J |
| KEGG |
D00059 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:15765 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1009 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.405 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
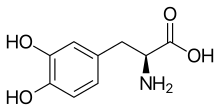
| Formula | C9H11NO4 |
| Molar mass | 197.19 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
L-DOPA (/ˌɛlˈdoʊpə/ or levodopa /ˌlɛvoʊˈdoʊpə/) (alt., L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) is an amino acid that is made and used as part of the normal biology of humans, some animals and plants. Some animals and humans make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid L-tyrosine. L-DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline) collectively known as catecholamines. Furthermore, L-DOPA itself mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS.L-DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as a psychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Pharmacopa, Atamet, Stalevo, Madopar, and Prolopa. As a drug, it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia.
...
Wikipedia
