Klumpke paralysis
| Klumpke's paralysis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
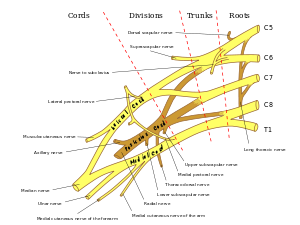
| Brachial plexus. Klumpke paralysis primarily affects C8 and T1. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | pediatrics |
| ICD-10 | P14.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 767.6 |
| DiseasesDB | 7200 |
Klumpke's paralysis (or Klumpke's palsy or Dejerine–Klumpke palsy) is a variety of partial of the lower roots of the brachial plexus. The brachial plexus is a network of spinal nerves that originates in the back of the neck, extends through the axilla (armpit), and gives rise to nerves to the upper limb. (see picture - click to enlarge). It is named after Augusta Déjerine-Klumpke.
Symptoms include intrinsic minus hand deformity,paralysis of intrinsic hand muscles, and C8/T1 Dermatome distribution numbness. Involvement of T1 may result in Horner's syndrome, with ptosis, and miosis. Weakness or lack of ability to use specific muscles of the shoulder or arm.It can be contrasted to Erb-Duchenne's palsy, which affects C5 and C6.
Klumpke's paralysis is a form of paralysis involving the muscles of the forearm and hand, resulting from a brachial plexus injury in which the eighth cervical (C8) and first thoracic (T1) nerves are injured either before or after they have joined to form the lower trunk. The subsequent paralysis affects, principally, the intrinsic muscles of the hand (notably the interossei, thenar and hypothenar muscles) and the flexors of the wrist and fingers (notably flexor carpi ulnaris and ulnar half of the flexor digitorum profundus). Forearm pronators and wrist flexors may be involved, as may dilators of the iris and elevators of the eyelid (both of which may be seen in the case of associated Horner's syndrome). The classic presentation of Klumpke's palsy is the “claw hand” where the forearm is supinated and the wrist and fingers are flexed. If Horner syndrome is present, there is miosis (constriction of the pupils) in the affected eye.
...
Wikipedia
