Karstedt’s catalyst
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Properties | |
| C24H54O3Pt2Si6 | |
| Molar mass | 949.4 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.74 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 12 to 13 °C (54 to 55 °F; 285 to 286 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Karstedt's catalyst is an organoplatinum compound derived from divinyl-containing disiloxane. This coordination complex is widely used in hydrosilylation catalysis. It is a colorless solid that is generally assumed to be a mixture of related Pt(0) alkene complexes. The catalyst is named after Bruce D. Karstedt, who developed it in the early 1970s while working for General Electric.
Carbon-silicon bonds are created via hydrosilylation reactions. This reaction has very important applications to industry. While it is favorable thermodynamically, hydrosilylation does not proceed in the absence of a catalyst. It is produced by treatment of chloroplatinic acid by the divinyltetramethyldisiloxane.
The catalyst can also be used in a reductive amination reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine with phenylsilane as the reducing agent.
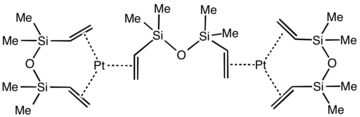
The oxidation state of the platinum is 0. Using X-ray crystallography, the structure of the complex Pt2[(Me2SiCH=CH2)2O]3 has been confirmed. Each Pt(0) center is surrounded by three alkene ligands. The Pt center and six coordinated carbon atoms are approximately coplanar, as found for simpler complexes such as Pt(C2H4)3.
...
Wikipedia
