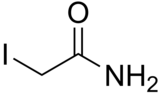
Iodoacetamide
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Iodoacetamide
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.119 |
| EC Number | 205-630-1 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | AC4200000 |
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C2H4INO | |
| Molar mass | 184.96 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white crystals (yellow colouration indicates the presence of iodine) |
| Melting point | 94 °C (201 °F; 367 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | brief MSDS, extended MSDS |
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
2-Iodoacetamide is an alkylating agent used for peptide mapping purposes. Its actions are similar to those of iodoacetate. It is commonly used to bind covalently with the thiol group of cysteine so the protein cannot form disulfide bonds. Also used in ubiquitin studies as an inhibitor of deubiquitinase enzymes (DUBs) because it alkylates the cysteine residues at the DUB active site.
Iodoacetamide is an irreversible inhibitor of all cysteine peptidases, with the mechanism of inhibition occurring from alkylation of the catalytic cysteine residue (see schematic). In comparison with its acid derivative, iodoacetate, iodoacetamide reacts substantially more quickly. This observation appears contradictory to standard chemical reactivity, however the presence of a favourable interaction between the positive imidazolium ion of the catalytic histidine and the negatively charged carboxyl-group of the iodoacetate is the reason for the increased relative activity of iodoacetamide.
...
Wikipedia

