Intrauterine hypoxia
| Intrauterine hypoxia | |
|---|---|
 |
|
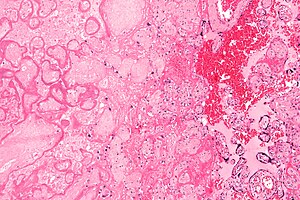
| Micrograph of a placental infarct (left of image), a cause of intrauterine hypoxia. H&E stain. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | pediatrics |
| ICD-10 | P20 |
| ICD-9-CM | 768 |
Intrauterine hypoxia occurs when the fetus is deprived of an adequate supply of oxygen. It may be due to a variety of reasons such as prolapse or occlusion of the umbilical cord, placental infarction and maternal smoking. Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) may cause or be the result of hypoxia. Intrauterine hypoxia can cause cellular damage that occurs within the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). This results in an increased mortality rate, including an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Oxygen deprivation in the fetus and neonate have been implicated as either a primary or as a contributing risk factor in numerous neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as epilepsy, ADHD, eating disorders and cerebral palsy.
There are various causes for intrauterine hypoxia (IH). The most preventable cause is maternal smoking. Cigarette smoking by expectant mothers has been shown to have a wide variety of deleterious effects on the developing fetus. Among the negative effects are carbon monoxide induced tissue hypoxia and placental insufficiency which causes a reduction in blood flow from the uterus to the placenta thereby reducing the availability of oxygenated blood to the fetus. Placental insufficiency as a result of smoking has been shown to have a causal effect in the development of pre-eclampsia. While some previous studies have suggested that carbon monoxide from cigarette smoke may have a protective effect against preeclampsia, a recent study conducted by the Genetics of Pre-Eclampsia Consortium (GOPEC) in the United Kingdom found that smokers were five times more likely to develop pre-eclampsia.Nicotine alone has been shown to be a teratogen which affects the autonomic nervous system, leading to increased susceptibility to hypoxia-induced brain damage. Maternal anemia in which smoking has also been implicated is another factor associated with IH/BA. Smoking by expectant mothers causes a decrease in maternal nucleated red blood cells (NRBC), thereby reducing the amount of red blood cells available for oxygen transport.
...
Wikipedia
