International Standard Serial Number (identifier)
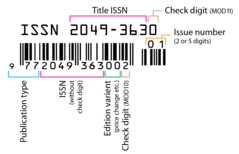
an ISSN, 2049-3630, as represented by an EAN-13 bar code. NOTE: MOD10 in the image should be MOD11.
|
|
| Acronym | ISSN |
|---|---|
| No. issued | > 2,000,000 |
| Introduced | 1976 |
| Managing organisation | ISSN International Centre |
| No. of digits | 8 |
| Check digit | Weighted sum |
| Example | 2049-3630 |
| Website | www |
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit serial number used to uniquely identify a serial publication. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSN are used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature.
The ISSN system was first drafted as an International Organization for Standardization (ISO) international standard in 1971 and published as ISO 3297 in 1975. ISO subcommittee TC 46/SC 9 is responsible for maintaining the standard.
When a serial with the same content is published in more than one media type, a different ISSN is assigned to each media type. For example, many serials are published both in print and electronic media. The ISSN system refers to these types as print ISSN (p-ISSN) and electronic ISSN (e-ISSN), respectively. Conversely, as defined in ISO 3297:2007, every serial in the ISSN system is also assigned a linking ISSN (ISSN-L), typically the same as the ISSN assigned to the serial in its first published medium, which links together all ISSNs assigned to the serial in every medium.
The format of the ISSN is an eight digit code, divided by a hyphen into two four-digit numbers. As an integer number, it can be represented by the first seven digits. The last code digit, which may be 0-9 or an X, is a check digit. Formally, the general form of the ISSN code (also named "ISSN structure" or "ISSN syntax") can be expressed as follows:
or by a PCRE regular expression:
The ISSN of the journal Hearing Research, for example, is 0378-5955, where the final 5 is the check digit, that is C=5. To calculate the check digit, the following algorithm may be used:
...
Wikipedia
