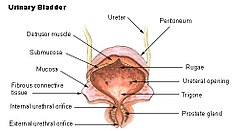
Internal sphincter muscle of urethra
| Internal urethral sphincter | |
|---|---|

Coronal section of anterior part of pelvis, through the pubic arch. Coronal section. (Region visible, but muscle not labeled.)
|
|
Urinary bladder (Region visible, but muscle not labeled.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Origin | The inferior ramus of the pubic bone |
| Insertion | Perineal raphe |
| Nerve | Sympathetics from L1-L2 through lumbar splanchnic nerves. Parasympathetics from S2-S4 through inferior hypogastric plexus. |
| Actions | Sympathetic contracts and parasympathetic relaxes the muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus sphincter urethrae internus |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
m_22/13540450 |
| TA |
A09.2.03.009 A09.4.02.013 |
| FMA | 45769 |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
The internal urethral sphincter is a urethral sphincter muscle which constricts the internal urethral orifice. It is the junction of the urethra with the urinary bladder surrounding the membranous urethra. The muscle is made of smooth muscle, so therefore it is under involuntary control. It is kept tonically contracted by lumbar plexus of the sympathetic nervous system.
During urination it is relaxed via branches from the inferior hypogastric plexus (S2-S4) parasympathetic nervous system. This is the primary muscle for maintenance of continence of urine. It prevents urine leakage as the muscle is contracted via sympathetic stimulation from the lumbar splanchnic nerves. During ejaculation, it contracts to prevent reflux of semen into the urinary bladder, a phenomenon called retrograde ejaculation.
Because the internal urethral sphincter is under involuntary control, it is believed to play a role in paruresis, in which a person who perceives himself to be under observation is unable to urinate.
...
Wikipedia
