Infratentorial neoplasms
| Cerebellar tentorium | |
|---|---|
 |
|
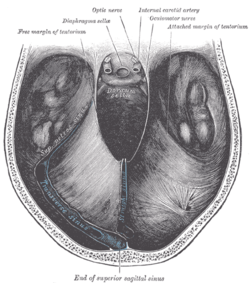
Cerebellar tentorium seen from above.
|
|
| Details | |
| Part of | Meninges |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Tentorium cerebelli |
| NeuroNames | ancil-261 |
| TA | A14.1.01.104 |
| FMA | 83966 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
The cerebellar tentorium or tentorium cerebelli (Latin: "tent of the cerebellum") is an extension of the dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the inferior portion of the occipital lobes.
The cerebellar tentorium is an arched , elevated in the middle, and inclining downward toward the circumference.
It covers the top of the cerebellum, and supports the occipital lobes of the brain.
Its anterior border is free and concave, and bounds a large oval opening, the tentorial incisure, for the transmission of the cerebral peduncles.
It is attached, behind, by its convex border, to the transverse ridges upon the inner surface of the occipital bone, and there encloses the transverse sinuses; in front, to the superior angle of the petrous part of the temporal bone on either side, enclosing the superior petrosal sinuses.
At the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone the free and attached borders meet, and, crossing one another, are continued forward to be fixed to the anterior and posterior clinoid processes (respectively) of the sphenoid bone.
To the middle line of its upper surface the posterior border of the falx cerebri is attached, the straight sinus being placed at their line of junction.
Brain tumors are often characterized as supratentorial (above the tentorium) and infratentorial (below the tentorium). The location of the tumor can help in determining the type of tumor, as different tumors occur with different frequencies at each location. Additionally, most childhood primary brain tumors are infratentorial, while most adult primary brain tumors are supratentorial. The location of the tumor may have prognostic significance as well.
...
Wikipedia
