Indometacin
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
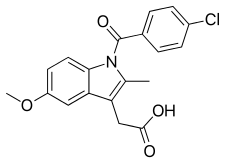
2-{1-[(4-Chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl}acetic acid
|
|
| Clinical data | |
| Pronunciation | /ɪndoʊˈmɛtəsᵻn/ |
| Trade names | Indocid, Indocin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral, rectal, IV, topical |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~100% (oral), 80–90% (rectal) |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 2.6-11.2 hours (adults), 12-28 hours (infants) |
| Excretion | Renal (60%), fecal (33%) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
53-86-1 |
| ATC code | C01EB03 (WHO) M01AB01 (WHO), M02AA23 (WHO), S01BC01 (WHO) |
| PubChem | CID 3715 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 1909 |
| DrugBank |
DB00328 |
| ChemSpider |
3584 |
| UNII |
XXE1CET956 |
| KEGG |
D00141 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:49662 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL6 |
| PDB ligand ID | IMN (PDBe, RCSB PDB) |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C19H16ClNO4 |
| Molar mass | 357.787 g.mol−1 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
Indometacin (INN and BAN) or indomethacin (AAN, USAN and former BAN) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used as a prescription medication to reduce fever, pain, stiffness, and swelling from inflammation. It works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, molecules known to cause these symptoms.
It is marketed under more than twelve different trade names. As of 2015 the cost for a typical month of medication in the United States is less than 25 USD.
Clinical indications for indometacin include:
Indometacin has also been used clinically to delay premature labor, reduce amniotic fluid in polyhydramnios, and to close patent ductus arteriosus.
Indometacin is a potent drug with many serious side effects and should not be considered an analgesic for minor aches and pains or fever. The medication is better described as an anti-inflammatory, rather than an analgesic. Indometacin can also affect warfarin and subsequently raise INR.
Since indometacin inhibits both cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2, it inhibits the production of prostaglandins in the stomach and intestines, which maintain the mucous lining of the gastrointestinal tract. Indometacin, therefore, like other non-selective COX inhibitors can cause peptic ulcers. These ulcers can result in serious bleeding and/or perforation requiring hospitalization of the patient.
...
Wikipedia
