Indium(III) bromide
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Indium(III) bromide
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
13465-09-3 |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.343 |
| EC Number | 236-692-8 |
| PubChem | 26046 |
| Properties | |
| InBr3 | |
| Molar mass | 354.530 g/mol |
| Appearance | hygroscopic yellow-white monoclinic crystals |
| Density | 4.74 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 420 °C (788 °F; 693 K) |
| 414 g/100 mL at 20 °C | |
| −107.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
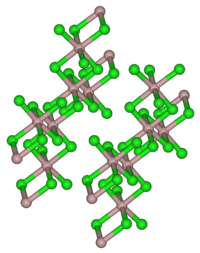
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, mS16 | |
| C12/m1, No. 12 | |
| Thermochemistry | |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
-428.9 kJ·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other cations
|
indium(III) fluoride indium(III) chloride indium(III) iodide |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Indium(III) bromide, (indium tribromide), InBr3, is a chemical compound of indium and bromine. It is a Lewis acid and has been used in organic synthesis.
It has the same crystal structure as aluminium trichloride, with 6 coordinate indium atoms. When molten it is dimeric, In2Br6, and it is predominantly dimeric in the gas phase. The dimer has bridging bromine atoms with a structure similar to dimeric aluminium trichloride Al2Cl6.
It is formed by the reaction of indium and bromine. InBr3 forms complexes with ligands, L, InBr3L, InBr3L2, InBr3L3.
Reaction with indium metal forms lower valent indium bromides, InBr2, In4Br7, In2Br3, In5Br7, In7Br9, indium(I) bromide. In refluxing xylene solution InBr3 and In metal react to form InBr2.
...
Wikipedia
