Imipenem
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Primaxin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a686013 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
IM, IV |
| ATC code | J01DH51 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 20% |
| Metabolism | Renal |
| Biological half-life | 38 minutes (children), 60 minutes (adults) |
| Excretion | Urine (70%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
64221-86-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5282372 |
| DrugBank |
DB01598 |
| ChemSpider |
4445535 |
| UNII |
Q20IM7HE75 |
| KEGG |
D00206 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:51799 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL43708 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.205.470 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
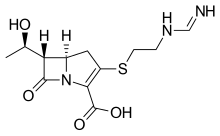
| Formula | C12H17N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 299.347 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
Imipenem (Primaxin) is an intravenous β-lactam antibiotic discovered by Merck scientists Burton Christensen, William Leanza, and Kenneth Wildonger in the mid-1970s. It was the first member of the carbapenem class of antibiotics. Carbapenems are highly resistant to the β-lactamase enzymes produced by many multiple drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, thus play a key role in the treatment of infections not readily treated with other antibiotics.
Imipenem was patented in 1975. It was discovered via a lengthy trial-and-error search for a more stable version of the natural product thienamycin, which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces cattleya. Thienamycin has antibacterial activity, but is unstable in aqueous solution, so impractical to administer to patients. Imipenem has a broad spectrum of activity against aerobic and anaerobic, Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is particularly important for its activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the Enterococcus species. It is not active against MRSA, however.
Imipenem acts as an antimicrobial through inhibiting cell wall synthesis of various Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It remains very stable in the presence of β-lactamase (both penicillinase and cephalosporinase) produced by some bacteria, and is a strong inhibitor of β-lactamases from some Gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to most β-lactam antibiotics.
Acinetobacter anitratus, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Actinomyces odontolyticus, Aeromonas hydrophila, Bacteroides distasonis, Bacteroides uniformis, and Clostridium perfringens are generally susceptible to imipenem, while Acinetobacter baumannii, some Acinetobacter spp., Bacteroides fragilis, and Enterococcus faecalis have developed resistance to imipenem to varying degrees. Not many species are resistant to imipenem except Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Oman) and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.
...
Wikipedia
