Hydranencephaly
| Hydranencephaly Hydrancephaly |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
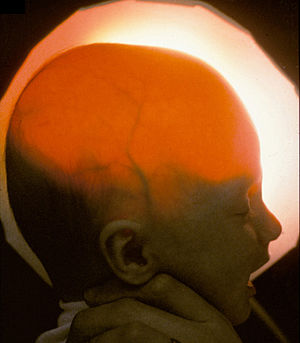
| Image of a baby with hydrancephaly, light passes through the skull indicating lack of forebrain. Courtesy of D. P. Agamanolis http://neuropathology-web.org" |
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q04.3 |
| ICD-9-CM | 742.3 |
| DiseasesDB | 31516 |
| eMedicine | radio/351 |
| MeSH | D006832 |
Hydranencephaly or hydrancephaly is a condition in which the brain's cerebral hemispheres are absent to varying degrees and the remaining cranial cavity is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Hydranencephaly (or hydrancephaly) is a type of cephalic disorder. These disorders are congenital conditions that derive from either damage to, or abnormal development of, the fetal nervous system in the earliest stages of development in utero. Cephalic is the medical term for “head” or “head end of body.” These conditions do not have any definitive identifiable cause factor; instead generally attributed to a variety of hereditary or genetic conditions, but also by environmental factors such as maternal infection, pharmaceutical intake, or even exposure to high levels of radiation.
This should not be confused with hydrocephalus, which is an accumulation of excess cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain.
In hemihydranencephaly, only half of the cranial cavity is filled with fluid.
Usually the cerebellum and brain stem are formed normally, although in some cases the cerebellum may also be absent. An infant with hydranencephaly may appear normal at birth or may have some distortion of the skull and upper facial features due to fluid pressure inside the skull. The infant's head size and spontaneous reflexes such as sucking, swallowing, crying, and moving the arms and legs may all seem normal, depending on the severity of the condition. However, after a few weeks the infant sometimes becomes irritable and has increased muscle tone (hypertonia). After several months of life, seizures and hydrocephalus may develop, if they did not exist at birth. Other symptoms may include visual impairment, lack of growth, deafness, blindness, spastic quadriparesis (paralysis), and intellectual deficits.
Some infants may have additional abnormalities at birth including seizures, myoclonus (involuntary sudden, rapid jerks), limited thermoregulation abilities, and respiratory problems.
...
Wikipedia
