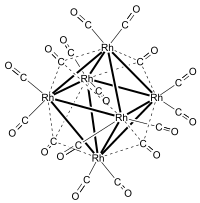
Hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium
|
|
| Other names
Hexarhodium hexadecacarbonyl
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.539 |
| Properties | |
| C16O16Rh6 | |
| Molar mass | 1065.62 g/mol |
| Appearance | Black crystals |
| Melting point | 235 °C (455 °F; 508 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium is a metal carbonyl cluster with the formula Rh6(CO)16. It exists as black crystals that are soluble in organic solvents.
Rh6(CO)16 was first prepared by Heiber in 1943 by carbonylation of RhCl3·3H2O at 80-230 °C and 200 atm carbon monoxide with silver or copper as a halide acceptor. It was incorrectly formulated as Rh4(CO)11. Subsequently, the carbonylation of a mixture of anhydrous rhodium trichloride and iron pentacarbonyl was shown to give good yields of Rh6(CO)16. Other compounds of rhodium are also effective precursors such as Rh2Cl2(CO)4 and rhodium(II) acetate:
Rh6(CO)16 catalyzes a number of organic reactions including hydrogenation and hydroformylation.
...
Wikipedia
