Hesselbach's triangle
| Inguinal triangle | |
|---|---|

Internal (from posterior to anterior) view of right inguinal area of the male pelvis.
Inguinal triangle is labeled in green. The three surrounding structures: inferior epigastric vessels: Run from upper left to center. inguinal ligament: Runs from upper right to bottom left. rectus abdominis muscle: Runs from upper left to bottom left, labeled rectus at upper left. |
|
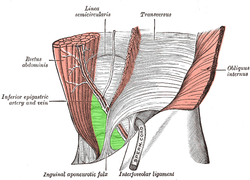
External view.
Inguinal triangle is labeled in green. Borders: inferior epigastric artery and vein: labeled at center left, and run from upper right to bottom center. inguinal ligament: not labeled on diagram, but runs a similar path to the inguinal aponeurotic falx, labeled at bottom. rectus abdominis muscle: runs from upper left to bottom left. |
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | trigonum inguinale |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
t_19/12823490 |
| TA | A10.1.02.433 |
| FMA | 256506 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
In human anatomy, the inguinal triangle is a region of the abdominal wall. It is also known by the eponym Hesselbach's triangle, after Franz Kaspar Hesselbach.
It is defined by the following structures:
This can be remembered by the mnemonic RIP (Rectus sheath (lateral border), Inferior epigastric artery, Poupart's ligament (inguinal ligament)).
The inguinal triangle contains a depression referred to as the medial inguinal fossa, through which direct inguinal hernias protrude through the abdominal wall.
...
Wikipedia
