Hernandiaceae
| Hernandiaceae | |
|---|---|
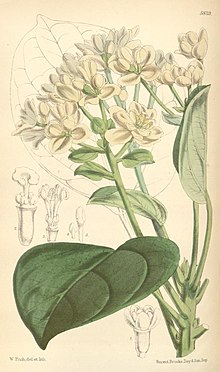 |
|
| Hernandia moerenhoutiana | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Magnoliids |
| Order: | Laurales |
| Family: |
Hernandiaceae Blume |
| genera | |
The Hernandiaceae are a family of flowering plants, angiosperms, in the order Laurales. Consisting of five genera with caabout 58 known species, they are distributed over the world's tropical areas, some of them widely distributed in coastal areas, but they occur from sea level to over 2000 m.
The family is closely related to the Lauraceae, and many species inhabit laurel forest habitat; they have laurel-like (lauroid) leaves. Based on morphology, chromosome numbers, geographical distribution, and phylogenetic analyses, the family is clearly divided into two groups that have been given the rank of subfamilies Gyrocarpoideae and Hernandioideae.
The Hernandaceae are important components of tropical forests ranging from low-lying to montane forests.
Because of the special lack of worldwide knowledge about the family in general, little is known about their diversity yet. The knowledge of this family to national level, is that to be expected in countries with limited economic means with the vast majority of species indeterminate or even poorly determined. Recently described new species come from collections made in countries with limited economic means. Therefore, an increase in the study of family, at national level, is of utmost importance for the progress of the systematics of the family in general. Trees of the Hernandiaceae family predominate in the world's laurel forests and cloud forests, which occur in tropical, subtropical, and mild temperate regions of the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, highlighting the African, Indian, and Pacific Ocean islands, New Caledonia, Madagascar, and central Chile.
The main economical uses for this family are essential oils, found in many species that are important for spices and perfumes, and the hardwood of many species is a source for timber around the world. A great number of species is in danger of extinction due to overexploitation as medicinal plants or timber extraction and loss of habitat.
The Hernandiaceae are a very important family; their species inhabit the ecosystems with monoecious, rarely dioecious, deciduous or evergreen trees, shrubs, and perennial climbing plants. The mode of dispersion is variable among the species. Most species of genus Hernandia have red domes, suggesting zoochory, while Hernandia guianensis is hydrochorian in fresh water, and H. nymphaeifolia and Gyrocarpus americanus are hydrochorian in sea water.
...
Wikipedia
