Heptagon
| Regular heptagon | |
|---|---|
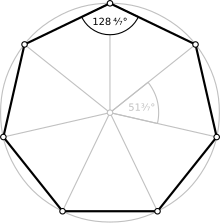
A regular heptagon
|
|
| Type | Regular polygon |
| Edges and vertices | 7 |
| Schläfli symbol | {7} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | Dihedral (D7), order 2×7 |
| Internal angle (degrees) | ≈128.571° |
| Dual polygon | Self |
| Properties | Convex, cyclic, equilateral, isogonal, isotoxal |
In geometry, a heptagon is a seven-sided polygon or 7-gon.
The heptagon is also occasionally referred to as the septagon, using "sept-" (an elision of , a Latin-derived numerical prefix, rather than , a Greek-derived numerical prefix) together with the Greek suffix "-agon" meaning angle.
A regular heptagon, in which all sides and all angles are equal, has internal angles of 5π/7 radians (128.5714286 degrees). Its Schläfli symbol is {7}.
The area (A) of a regular heptagon of side length a is given by:
This can be seen by subdividing the unit-sided heptagon into seven triangular "pie slices" with vertices at the center and at the heptagon's vertices, and then halving each triangle using the apothem as the common side. The apothem is half the cotangent of and the area of each of the 14 small triangles is one-fourth of the apothem.
The exact algebraic expression, starting from the cubic polynomial x3 + x2 − 2x − 1 (one of whose roots is ) is given in complex numbers by:
...
Wikipedia


