Heart disorders
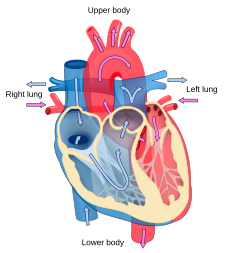
Blood flow diagram of the human heart. Blue components indicate de-oxygenated blood pathways and red components indicate oxygenated blood pathways.
|
|
| System | Cardiovascular |
|---|---|
| Subdivisions | Interventional, Nuclear |
| Significant diseases | Heart disease, Cardiovascular disease, Atherosclerosis, Cardiomyopathy, Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) |
| Significant tests | Blood tests, Electrophysiology study, Cardiac imaging, ECG, Echocardiograms, Stress test |
| Specialist | Cardiologist |
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
| Names | Doctor, Medical Specialist |
|
Occupation type
|
Specialty |
|
Activity sectors
|
Medicine |
| Description | |
|
Education required
|
|
|
Fields of
employment |
Hospitals, Clinics |
Cardiology (from Greek καρδίᾱ kardiā, "heart" and -λογία , "study") is a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the heart as well as parts of the circulatory system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery.
Although the cardiovascular system is inextricably linked to blood, cardiology is relatively unconcerned with hematology and its diseases. Some obvious exceptions that affect the function of the heart would be blood tests (electrolyte disturbances, troponins), decreased oxygen carrying capacity (anemia, hypovolemic shock), and coagulopathies.
All cardiologists study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders are through different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are inadequately trained to take care of adults. The surgical aspects are not included in cardiology and are in the domain of cardiothoracic surgery. For example, coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG), cardiopulmonary bypass and valve replacement are surgical procedures performed by surgeons, not cardiologists. However the insertion of stents, pacemakers are performed by cardiologists
...
Wikipedia
