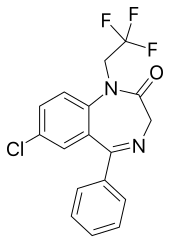
Halazepam
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a684001 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Biological half-life | 14 hours (halazepam), 50–100 hours (metabolites). |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | 9-chloro-6-phenyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-2,5-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undeca-5,8,10,12-tetraen-3-one |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.281 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H12ClF3N2O |
| Molar mass | 352.7 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Halazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative that was marketed under the brand names Paxipam in the United States,Alapryl in Spain, and Pacinone in Portugal.
Halazepam was used for the treatment of anxiety.
Adverse effects include drowsiness, confusion, dizziness, and sedation. Gastrointestinal side effects have also been reported including dry mouth and nausea.
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics were listed in Current Psychotherapeutic Drugs published in June 15, 1998 as follows:
Halazepam is classified as a schedule 4 controlled substance with a corresponding code 2762 by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
Halazepam was invented by Schlesinger Walter in the U.S. It was marketed as an anti-anxiety agent in 1981. However, Halazepam is not commercially available in the United States because it was withdrawn by its manufacturer for poor sales.
...
Wikipedia
