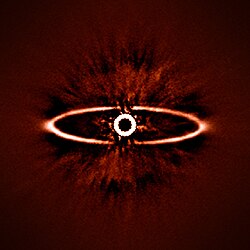
HR 4796
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 |
|
|---|---|
| Constellation | Centaurus |
| Right ascension | 12h 36m 01.03100s |
| Declination | −39° 52′ 10.2270″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.80 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A0 V_+ M2.5 V |
| B−V color index | +0.01 |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 9.4 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) |
RA: –56.66 mas/yr Dec.: –24.99 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 13.74 ± 0.33mas |
| Distance | 237 ± 6 ly (73 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 1.61±0.11 |
| Details | |
| Component A | |
| Mass | 2.18 ± 0.10 M☉ |
| Radius | 1.68 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 23 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.43 cgs |
| Temperature | 9,378 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.03 dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 152 km/s |
| Age | 8 ± 2 Myr |
| Component B | |
| Mass | 0.3 M☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
HR 4796 is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus. Parallax measurements put it at a distance of 237 light-years (73 parsecs) from the Earth. The two components of this system have an angular separation of 7.7 arcseconds, which, at their estimated distance, is equivalent to a projected separation of about 560 Astronomical Units (AU), or 560 times the separation of the Earth from the Sun. The star and its ring resemble an eye, and it is sometimes known by the nickname "Sauron's Eye".
This is a young system with an estimated age of about 8 million years. The primary member A has a stellar classification of A0 V, while its smaller companion B is a red dwarf with a classification of M2.5 V. The luminosity class of 'V' indicates that both stars belong to the main sequence and are generating energy through the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen at their cores. The primary is emitting this energy from its outer envelope at an effective temperature of about 9,378 K, which gives it the white hue characteristic of A-type stars. It has a radius about 168% of the radius of the Sun and 218% of the Sun's mass. By comparison, the secondary has only 30% of a solar mass. The abundance of elements other than hydrogen or helium, what astronomers term the star's metallicity, is similar to the proportion in the Sun.
...
Wikipedia