HMG-box
| HMG (high mobility group) box | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
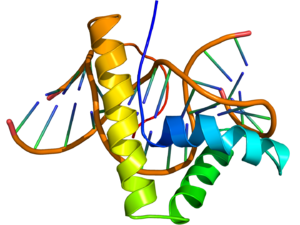
NMR structure of the HMG-box domain of the LEF1 protein (rainbow colored, N-terminus = blue, C-terminus = red) complexed with DNA (brown) based on the PDB: 2LEF coordinates.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | PF00505 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00505 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR009071 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1hsm | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1hsm | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
In molecular biology, the HMG-box (high mobility group box) is a protein domain which is involved in DNA binding.
The structure of the HMG-box domain contains three alpha helices separated by loops (see figure to the right).
HMG-box containing proteins only bind non-B-type DNA conformations (kinked or unwound) with high affinity. HMG-box domains are found in high mobility group proteins, which are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, and DNA repair, all of which require changing the conformation of chromatin. The single and the double box HMG proteins alter DNA architecture by inducing bends upon binding.
...
Wikipedia
