HCoV-EMC
| HCoV-EMC/2012 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
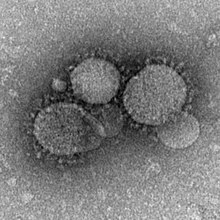
| MERS-CoV particles as seen by negative stain electron microscopy. Virions contain characteristic club-like projections emanating from the viral membrane. | |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group IV ((+)ssRNA) |
| Order: | Nidovirales |
| Family: | Coronaviridae |
| Subfamily: | Coronavirinae |
| Genus: | Betacoronavirus |
| Species: | HCoV-EMC/2012 |
HCoV-EMC/2012, or Human Coronavirus Erasmus Medical Center/2012 is the name of a novel strain of coronavirus isolated from the sputum of the first person to become infected with what was later named Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, or MERS-CoV.
An investigation of bat roosts in Bisha, the hometown of the index patient, by the Saudi Ministry of Health discovered an Egyptian tomb bat in a large roost close to the index patient's home. Phylogenetic analysis showed a 100% match between the virus isolated from the bat and HCoV-EMC/2012 isolated from the index patient.
HCoV-EMC/2012 is the sixth coronavirus known to infect humans and the first human virus within betacoronavirus lineage C. It is a new genotype which is related to bat coronaviruses, specifically an Egyptian tomb bat, and is not the same beta-CoV as the SARS-CoV, but is distantly related.
...
Wikipedia
