Grubbs' catalyst
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
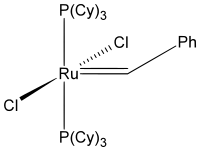
Benzylidene-bis(tricyclohexylphosphino)-dichlororuthenium
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
172222-30-9 |
|
| PubChem | 24881009 |
| Properties | |
| C43H72Cl2P2Ru | |
| Molar mass | 822.96 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Purple solid |
| Melting point | 153 °C (307 °F; 426 K) (decomposition) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
[1,3-bis-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-2-imidazolidinylidene]dichloro(phenylmethylene)(tricyclohexylphosphino)ruthenium
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 246047-72-3 | |
| Properties | |
| C46H65Cl2N2PRu | |
| Molar mass | 848,97 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Pinkish brown solid |
| Melting point | 143.5 to 148.5 °C (290.3 to 299.3 °F; 416.6 to 421.6 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
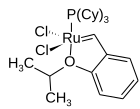
Dichloro(o-isopropoxyphenylmethylene)(tricyclohexylphosphine)ruthenium(II)
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 203714-71-0 | |
| PubChem | 24880901 |
| Properties | |
| C28H45Cl2OPRu | |
| Molar mass | 600.61 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Brown solid |
| Melting point | 195 to 197 °C (383 to 387 °F; 468 to 470 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
[1,3-Bis-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-2-imidazolidinylidene]dichloro(o-isopropoxyphenylmethylene)ruthenium
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 301224-40-8 | |
| Properties | |
| C31H38Cl2N2ORu | |
| Molar mass | 626.62 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Green solid |
| Melting point | 216 to 220 °C (421 to 428 °F; 489 to 493 K) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Grubbs' catalysts are a series of transition metal carbene complexes used as catalysts for olefin metathesis. They are named after Robert H. Grubbs, the chemist who first synthesized them. There are two generations of the catalyst, as shown on the right. In contrast to other olefin metathesis catalysts, Grubbs' catalysts tolerate other functional groups in the alkene, are air-tolerant and are compatible with a wide range of solvents. For these reasons, Grubbs' catalysts have become popular in synthetic organic chemistry.
The first well-defined ruthenium catalyst for olefin metathesis was discovered in 1992. It was prepared from RuCl2(PPh3)4 and diphenylcyclopropene.
This initial ruthenium catalyst was followed in 1995 by what is now known as the first-generation Grubbs catalyst. It is easily synthesized from RuCl2(PPh3)3, phenyldiazomethane, and tricyclohexylphosphine in a one-pot synthesis.
The first-generation Grubbs catalyst, while largely replaced by the second-generation catalyst in usage, was not only the first catalyst to be developed other than those developed by Richard R. Schrock (Schrock carbenes), but is also important as a precursor to all other Grubbs-type catalysts.
The second-generation catalyst has the same uses in organic synthesis as the first generation catalyst, but generally with higher activity. This catalyst is stable toward moisture and air, thus is easier to handle in the lab.
...
Wikipedia
